こんにちは。ゲームプログラマーのメガネです。
この記事では、iOSやAndroid向けのアプリを開発できるFlutterを利用して、リバーシを作る工程を解説します。
新しい言語や開発環境を学ぶときに、ある程度仕様を把握することは必要ですが、とりあえず何かを作ってみるのが圧倒的な成長に繋がります。
実は私もFlutterを使うのははじめてで、このリバーシを作りながら学びました。その知見を共有しますので、長いですが最後まで読んでもらえると嬉しいです。
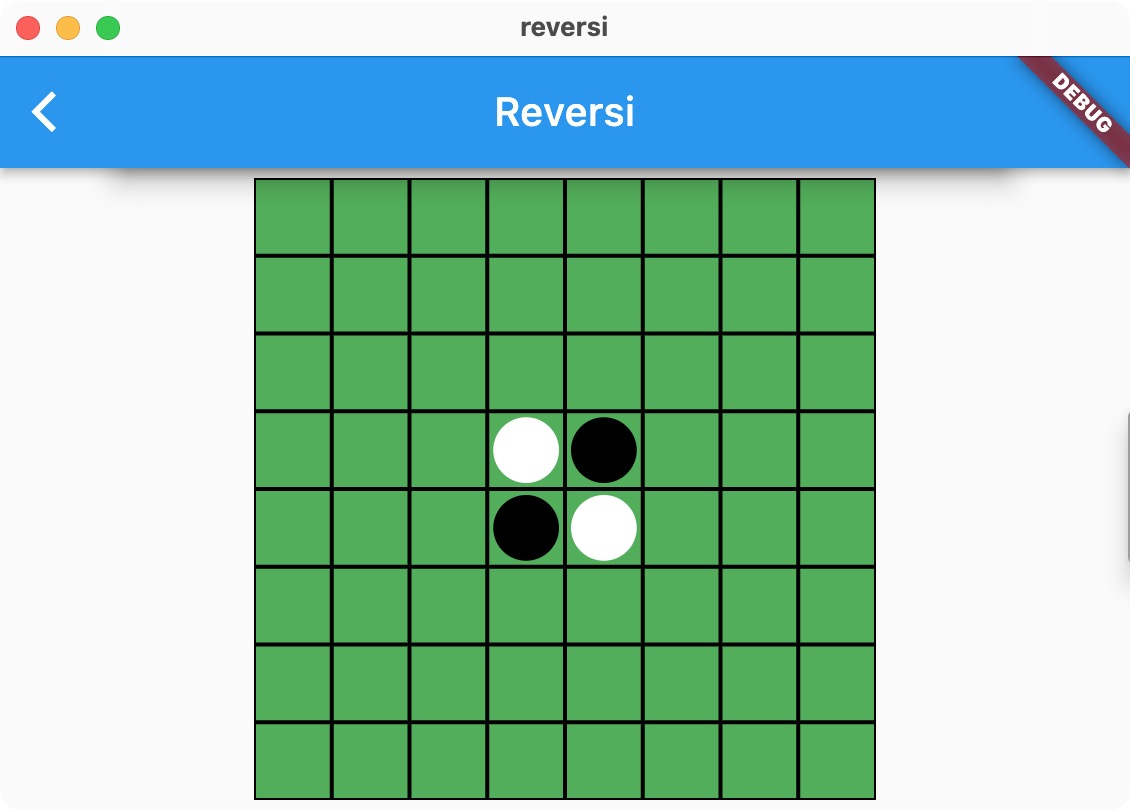
完成したリバーシ
はじめに、完成したリバーシを公開します。Web用にパブリッシュしました。
右下の「ゲームをはじめる」で開始します。白と黒が交互においていき、どちらもおけなくなったら終了です。
ソースコードはこちらです。
https://github.com/meganeprog/flutter_reversi
FlutterはiOS/Androidのアプリ開発を楽にするフレームワーク
Flutter(フラッター)はGoogleが開発した、クロスプラットフォーム対応のフレームワークです。
ネイティブアプリ開発において、iOSはSwift、AndroidはKotlinのように、それぞれ別の言語で開発する必要がありました。Flutterを使用することで大部分を共通のコードで書けるため、様々なプラットフォーム向けのアプリを楽に開発できるようになります。
対応するプラットフォームは以下のとおり。
- iOS
- Android
- Webアプリケーション
- Windows
- Mac
- Linux
プログラム言語はDartです。あまりメジャーではないですが、JavaやC++に近いオブジェクト思考言語です。オブジェクト思考言語を触ったことのある人は、すんなり覚えられると思います。
Flutterの環境構築
こちらを参考に。
https://www.sejuku.net/blog/123973
プロジェクトの作成
ではここから、リバーシの作り方を解説していきます。とりあえずプロジェクトの作成です。
Visual Studio Codeを起動して、メニューバーの「表示」から「コマンドパレット」を選択します。
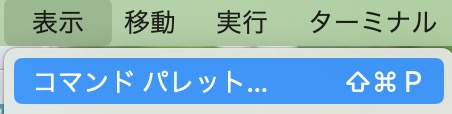
コマンドパレットに「Flutter」と入力し、「Flutter: New Project」を選択します。
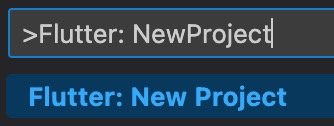
「Application」を選択します。
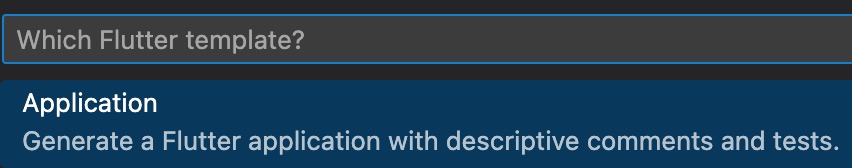
フォルダを選択します。
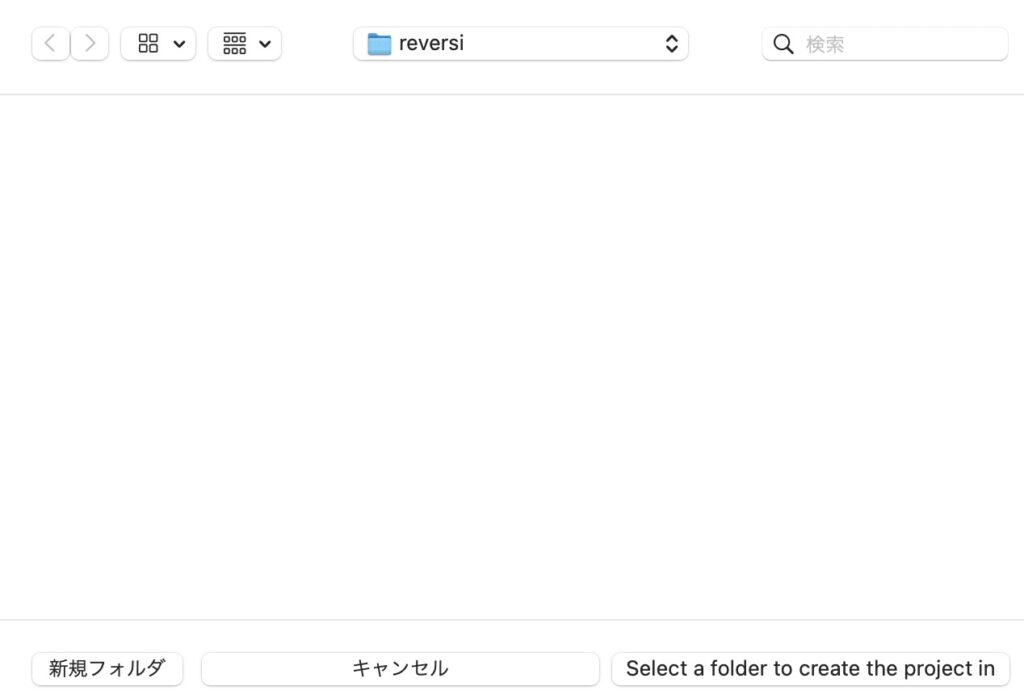
プロジェクト名を入力します。「reversi」と入力しEnterキーで決定します。
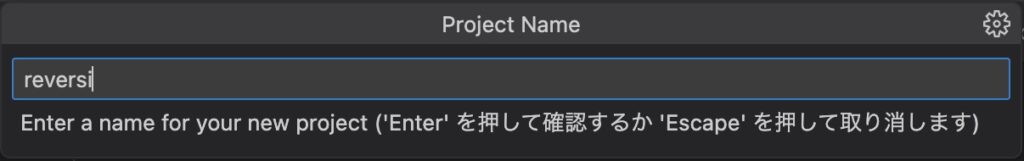
プロジェクトが作成され、初期化処理が行われます。
タイトルとゲームを遷移させる
今回のリバーシは、タイトル画面とゲーム画面だけのシンプルな画面構成です。
タイトル画面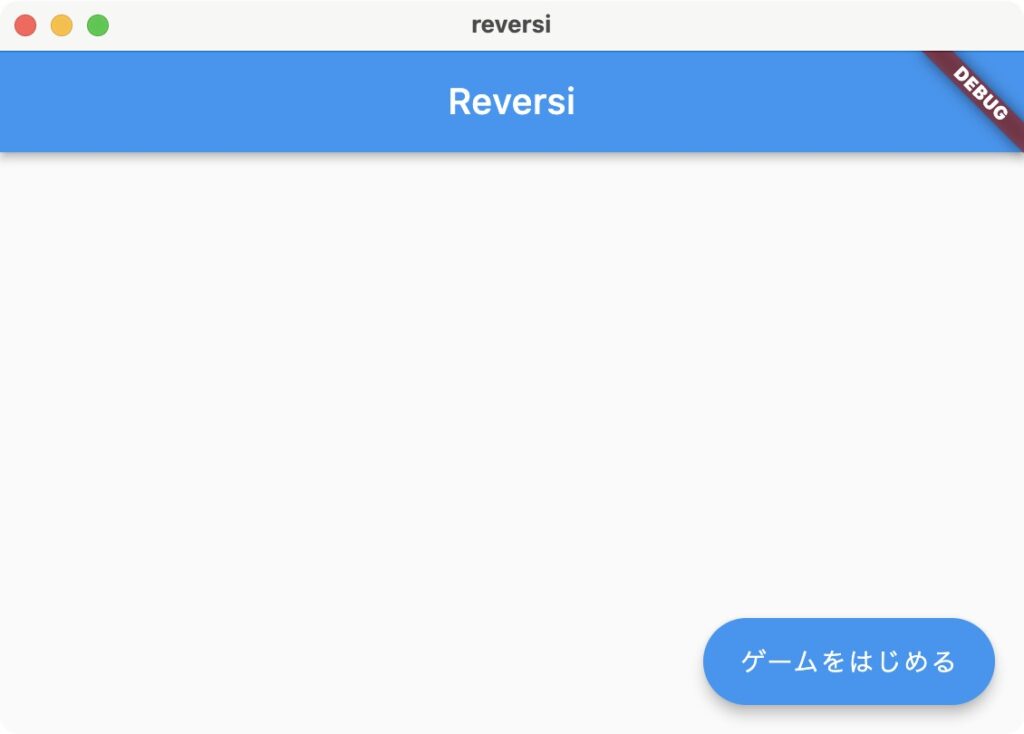 | ゲーム画面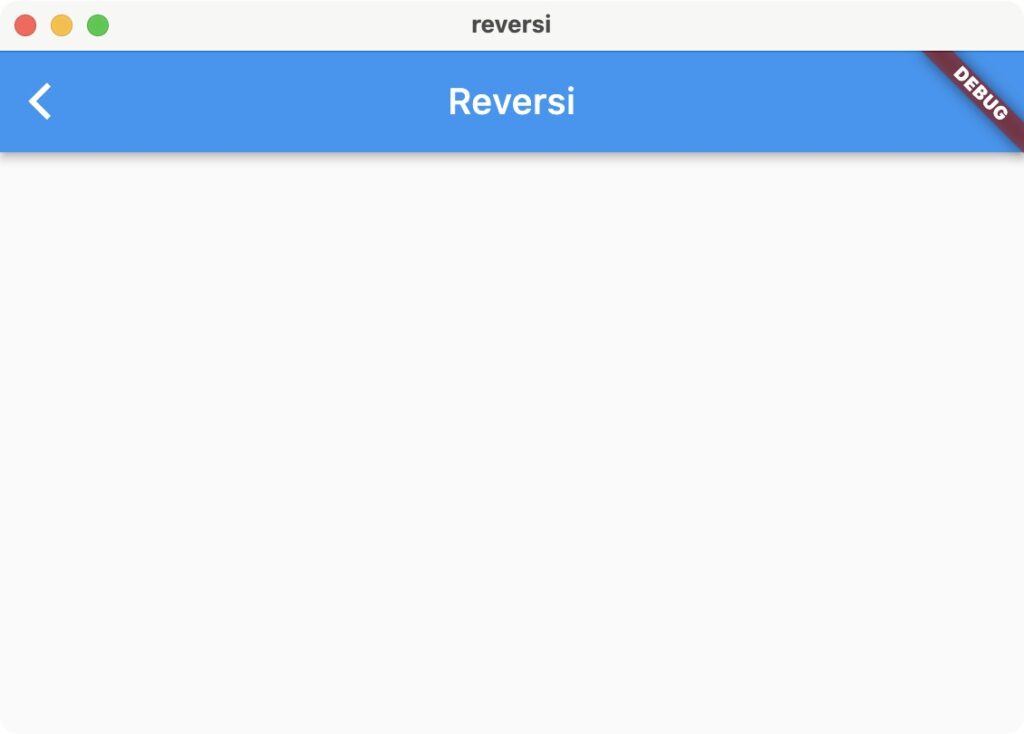 |
タイトルで「ゲームをはじめる」ボタンを押すと、ゲーム画面に遷移してゲームを開始します。ゲームを終了するときは、AppBarの左上の戻るボタンでタイトルに戻ります。
機種共通のコードはlib以下に配置します。今回のリバーシのコードは全てlib以下に配置しますので、以下の構成になります。
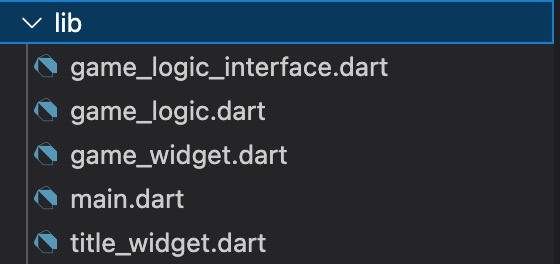
ゲーム画面のWidgetを作成
中身は後で実装するので、とりあえずゲーム画面のガワを作ります。
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
class GameWidget extends StatelessWidget {
const GameWidget({super.key});
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: const Text('Reversi'),
),
);
}
}タイトル画面のWidgetを作成
タイトル画面を作ります。タイトルは「ゲームをはじめる」ボタンが1つだけあり、押されたらゲーム画面に遷移するシンプルなものです。
画面遷移にはNavigator.pushNamedを使います。
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
class TitleWidget extends StatelessWidget {
const TitleWidget({super.key});
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: const Text('Reversi'),
),
floatingActionButton: FloatingActionButton.extended(
onPressed: () {
Navigator.pushNamed(context, 'game');
},
backgroundColor: Colors.blue,
label: const Text('ゲームをはじめる'),
),
);
}
}タイトルとゲームを行き来できるようにする
main.dartを以下のように変更します。routesに画面と名前を登録しておくことで、Navigator.pushNamed(context, 'game');のように名前で画面を遷移できるようになります。
Navigator.pushという命令でも遷移できるのですが、そうすると遷移先のクラスに依存してしまいます。コードを書くときは、できるだけ依存を減らすのが鉄則です。なのでpushNamedを利用りています。
Navigator.pushNamed(context, 'game');import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'title_widget.dart';
import 'game_widget.dart';
void main() {
runApp(MyApp());
}
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
MyApp({super.key});
// This widget is the root of your application.
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Reversi',
theme: ThemeData(
primarySwatch: Colors.blue,
),
routes: {
'title': (context) => const TitleWidget(),
'game': (context) => GameWidget(),
},
home: const TitleWidget(),
);
}
}おめでとうございます。これで、タイトルとゲームを行き来できるようになりました。
ゲームロジックのインターフェース
クラスをできるだけ依存させないのは、オブジェクト指向プログラミングの定石です。依存が少ないほどテストがしやすくなり、運用や保守をしやすくなります。
では、どのように依存を断ち切れば良いのかというと、インターフェースに依存させることです。インターフェースを介して具体的な実装を意識しなくても良いように作ります。
/// 石の状態
enum Stone {
blank, /// 何も置かれていない
white, /// 白
black, /// 黒
whiteHint, /// 白石を置く候補
blackHint, /// 黒石を置く候補
}
/// 石のポジションをあらわすクラス
class Position {
int row = 0;
int column =0;
Position(this.row, this.column);
}
/// ゲームロジックのインターフェース
abstract class GameLogicInterface {
/// 初期化
void init();
/// ボードの行数を取得する
int get boardRows;
/// ボードの列数を取得する
int get boardColumns;
/// 現在の番を取得する
Stone get turn;
/// 指定された場所の石を取得する
Stone getStone(int row, int column);
/// 置かれている石の数を取得する
int numberOfStone(Stone stone);
/// 指定された場所に石がおける場合に、裏返せる場所のリストを返す
///
/// 置ける場合は、裏返せる場所のリストを返す
/// 置けない場合は、空のリストを返す
List<Position> getReversePositions(int row, int column, Stone stone);
/// 指定された場所に石を置く
void putStone(int row, int column, Stone stone);
/// 指定された場所の石を裏返す
void reverseStone(int row, int column);
/// 次のターンへ
///
/// 双方とも打ち手がなくなったら false を返す
bool changeTurn();
/// 現在のターンで配置可能な場所にヒントを設定する
void hint();
/// ヒントをクリアする
void clearHint();
}ゲームロジックの実装
ここからゲームロジックの実装を解説します。
インターフェースを実装
GameLogicInterfaceを実装したGameLogicクラスを作成します。
implementsキーワードに続けて親クラスを書くことで、実装を行うことができます。
import 'game_logic_interface.dart';
/// ゲームロジックの実装
class GameLogic implements GameLogicInterface {
...
}ボードの初期化
Dartは配列をListであらわします。リバーシのボードは8×8マスなので、2次元配列を定義します。[]を代入することで、配列を直接初期化できます。
リバーシは中央の4マスに白と黒の石が2つずつ初期配置されますので、その位置に白と黒を置いています。Stone.blankとStone.blackが紛らわしいですが……、同じ文字数に揃えて配列を見やすくしています。
@overrideで親クラスの関数をオーバーライドできます。
late List<List<Stone>> _board; /// ボード
/// 初期化
@override
void init() {
_turn = Stone.white;
_board = [
[Stone.blank, Stone.blank, Stone.blank, Stone.blank, Stone.blank, Stone.blank, Stone.blank, Stone.blank],
[Stone.blank, Stone.blank, Stone.blank, Stone.blank, Stone.blank, Stone.blank, Stone.blank, Stone.blank],
[Stone.blank, Stone.blank, Stone.blank, Stone.blank, Stone.blank, Stone.blank, Stone.blank, Stone.blank],
[Stone.blank, Stone.blank, Stone.blank, Stone.white, Stone.black, Stone.blank, Stone.blank, Stone.blank],
[Stone.blank, Stone.blank, Stone.blank, Stone.black, Stone.white, Stone.blank, Stone.blank, Stone.blank],
[Stone.blank, Stone.blank, Stone.blank, Stone.blank, Stone.blank, Stone.blank, Stone.blank, Stone.blank],
[Stone.blank, Stone.blank, Stone.blank, Stone.blank, Stone.blank, Stone.blank, Stone.blank, Stone.blank],
[Stone.blank, Stone.blank, Stone.blank, Stone.blank, Stone.blank, Stone.blank, Stone.blank, Stone.blank],
];
} ボードの行数と列数
ボードの行数と列数を取得するゲッターです。
ゲッターはgetキーワードを付けて定義します。関数としてgetXXXと定義しても結果は同じですが、ゲッターを使った方が実行効率が良いです。
/// ボードの行数を取得する
@override
int get boardRows => _board.length;
/// ボードの列数を取得する
@override
int get boardColumns => _board[0].length;ターンの取得
現在白の番なのか黒の番なのか、ターンを取得するゲッターです。
_から始まる変数はプライベート変数です。プライベートにしておくことで、クラス外からのアクセスを禁止します。基本的には全てのメンバー変数はプライベートで問題なく、公開したい場合にゲッターを定義します。
Stone _turn = Stone.white; /// ターン
/// 現在のターンを取得する
@override
Stone get turn => _turn;指定の場所の石を取得
ボード上で指定された行、列の石を取得します。
assertはデバッグ中に条件がfalseになったときに、プログラムを停止させる命令です。停止した場合には、「アサーションに失敗した」と言います。assertを仕込んでおくことで、プログラマーが関数を誤って使用したことを早期に発見できます。
ここでは、行と列が範囲外の場合にアサーションに失敗するようにしています。
/// 指定された場所の石を取得する
@override
Stone getStone(int row, int column) {
assert(row >= 0 && row < boardRows && column >= 0 && column < boardColumns);
return _board[row][column];
}置かれている石の数を取得
stoneにStone.whiteかStone.blackを指定して、置かれている石の数を取得します。
for (var 変数 in 配列)という書き方で、配列の要素を巡回できます。
/// 置かれている石の数を取得する
@override
int numberOfStone(Stone stone)
{
int count = 0;
for (var rows in _board) {
for (var item in rows) {
if (item == stone) {
count++;
}
}
}
return count;
}石を置いた場合に裏返せる場所のリストを取得
指定の場所に石を置いた場合に、裏返せる石をリストアップします。縦横斜めを力技で調べているだけの、単純なアルゴリズムです。
_から始まる関数はプライベートメンバー関数です。変数と同様にクラスの外からは見えなくなります。具体的な実装を隠蔽する場合はプライベートにします。
/// 指定された場所に石がおける場合に、裏返せる場所のリストを返す
///
/// 置ける場合は、裏返せる場所のリストを返す
/// 置けない場合は、空のリストを返す
@override
List<Position> getReversePositions(int row, int column, Stone stone) {
assert(row >= 0 && row < boardRows && column >= 0 && column < boardColumns);
assert(stone != Stone.blank);
List<Position> reversePositions = List<Position>.empty(growable: true);
reversePositions.addAll(_getReversePositions(row, column, -1, 0, stone)); // 左方向
reversePositions.addAll(_getReversePositions(row, column, 1, 0, stone)); // 右方向
reversePositions.addAll(_getReversePositions(row, column, 0, -1, stone)); // 上方向
reversePositions.addAll(_getReversePositions(row, column, 0, 1, stone)); // 下方向
reversePositions.addAll(_getReversePositions(row, column, -1, -1, stone)); // 左上方向
reversePositions.addAll(_getReversePositions(row, column, -1, 1, stone)); // 左下方向
reversePositions.addAll(_getReversePositions(row, column, 1, -1, stone)); // 右上方向
reversePositions.addAll(_getReversePositions(row, column, 1, 1, stone)); // 右下方向
return reversePositions;
}
List<Position> _getReversePositions(int row, int column, int rowDir, int columnDir, Stone stone) {
Stone oppositeStone = stone == Stone.white ? Stone.black : Stone.white;
List<Position> reversePositions = List<Position>.empty(growable: true);
while (true) {
row += rowDir;
column += columnDir;
if (row < 0 || row >= boardRows || column < 0 || column >= boardColumns) {
// 端に到達したら置けない
return List<Position>.empty();
}
if (_board[row][column] == oppositeStone) {
// 進行方向に別の色の石があればリストに追加
reversePositions.add(Position(row, column));
}
else if (_board[row][column] == stone) {
// 1個でも別の色の石があれば置ける
return reversePositions;
}
else {
// 何も置かれていない場所に到達したら置けない
return List<Position>.empty();
}
}
}指定の場所に石を置く
指定の場所に石を置く関数です。
/// 指定された場所に石を置く
@override
void putStone(int row, int column, Stone stone) {
assert(row >= 0 && row < boardRows && column >= 0 && column < boardColumns);
assert(stone == Stone.black || stone == Stone.white);
_board[row][column] = stone;
}指定の場所の石を裏返す
白を黒に、黒を白に裏返します。
/// 指定された場所の石を裏返す
@override
void reverseStone(int row, int column)
{
assert(row >= 0 && row < boardRows && column >= 0 && column < boardColumns);
assert(_board[row][column] == Stone.black || _board[row][column] == Stone.white);
_board[row][column] = _board[row][column] == Stone.white ? Stone.black : Stone.white;
}次のターンにチェンジ
今が白の番だったら黒に、黒の番だったら白に変更します。白の人が置いた後に、黒が置けない場合は、もう一度白の番になるようにしています。
どちらも置けなくなったらfalseを返しており、その場合はゲーム終了です。
/// 次のターンへ
///
/// 双方とも打ち手がなくなったら false を返す
@override
bool changeTurn() {
clearHint();
Stone nextTurn = _turn == Stone.white ? Stone.black : Stone.white;
if (_canPut(nextTurn)) {
_turn = nextTurn;
return true;
}
// もう一度同じ人のターン
return _canPut(_turn);
}
bool _canPut(Stone stone) {
for (int row = 0; row < boardRows; row++) {
for (int column = 0; column < boardColumns; column++) {
if (_board[row][column] == Stone.blank) {
if (getReversePositions(row, column, stone).isNotEmpty) {
return true;
}
}
}
}
return false;
}ヒント
置ける場所を可視化するためのヒントを設定します。白を置ける場合はStone.whiteHint、黒を置ける場合はStone.blackHintを設定します。
また、次のターンに移るときにヒントをクリアするために、clearHint も作成します。
/// 現在のターンで配置可能な場所にヒントを設定する
@override
void hint() {
for (int row = 0; row < boardRows; row++) {
for (int column = 0; column < boardColumns; column++) {
if (_board[row][column] == Stone.blank) {
if (getReversePositions(row, column, _turn).isNotEmpty) {
_board[row][column] = _turn == Stone.black ? Stone.blackHint : Stone.whiteHint;
}
}
}
}
}
/// ヒントをクリアする
@override
void clearHint() {
for (int row = 0; row < boardRows; row++) {
for (int column = 0; column < boardColumns; column++) {
if (_board[row][column] == Stone.blackHint || _board[row][column] == Stone.whiteHint) {
_board[row][column] = Stone.blank;
}
}
}
}ゲーム画面のUIを作り込む
ここからは、最初に作成したGameWidgetを作り込んでいきます。
ロジックを受け取る
GameWidgetがGameLogicInterfaceを受け取るようにします。
GameLogicではなく、GameLogicInterfaceを受け取るのがポイントです。また、インスタンスをコンストラクタで受け取っています。これはDI(Dependency Injection)という手法です。
インターフェースを外から受け取ることによって、GameWidgetクラスはGameLogicのことを全く知らなくても動作します。GameLogicの実装が変わっても、GameWidgetへの変更は一切不要です。これがインターフェースに依存させて、外部から注入させる効果です。
/// ゲームのUI
class GameWidget extends StatefulWidget {
const GameWidget(this._gameLogic, {super.key});
@override
State<GameWidget> createState() => _GameWidgetState(_gameLogic);
final GameLogicInterface _gameLogic;
}
/// ゲームUIのステート
class _GameWidgetState extends State<GameWidget> {
_GameWidgetState(this._gameLogic);
@override
initState() {
super.initState();
_gameLogic.init();
}
final GameLogicInterface _gameLogic;
}main.dartでGameLogicのインスタンスを作成して、GameWidgetに渡してあげます。どこかでは必ずインスタンスを生成する必要がありますので、MyAppでやっています。なので、MyAppはGameLogicの変更をもろに受けてしまいますが、そういう層がどこかに必要になります。
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
MyApp({super.key});
// This widget is the root of your application.
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Reversi',
theme: ThemeData(
primarySwatch: Colors.blue,
),
routes: {
'title': (context) => const TitleWidget(),
'game': (context) => GameWidget(_gameLogic),
},
home: const TitleWidget(),
);
}
final GameLogicInterface _gameLogic = GameLogic();
}スクリーンサイズを取得する
スクリーンのサイズはMediaQuery.of(context).sizeで取得できます。AppBarを表示している場合は、そのサイズも考慮する必要があります。
/// スクリーンのサイズを取得する
Size _getScreenSize(BuildContext context) {
final double appBarHeight = AppBar().preferredSize.height;
final double screenWidth = MediaQuery.of(context).size.width;
final double screenHeight = MediaQuery.of(context).size.height - appBarHeight;
return Size(screenWidth, screenHeight);
}盤面のサイズを決める
スクリーンサイズの短い方のサイズに合わせて盤面のサイズを決定します。スマホのような縦長の画面の場合には、スクリーンの幅を盤面のサイズとしています。
/// 盤面のサイズを取得する
double _getBoardSize(BuildContext context) {
final Size screenSize = _getScreenSize(context);
final double boardSize = screenSize.width < screenSize.height ? screenSize.width : screenSize.height - 10.0;
return boardSize;
}盤面の表示
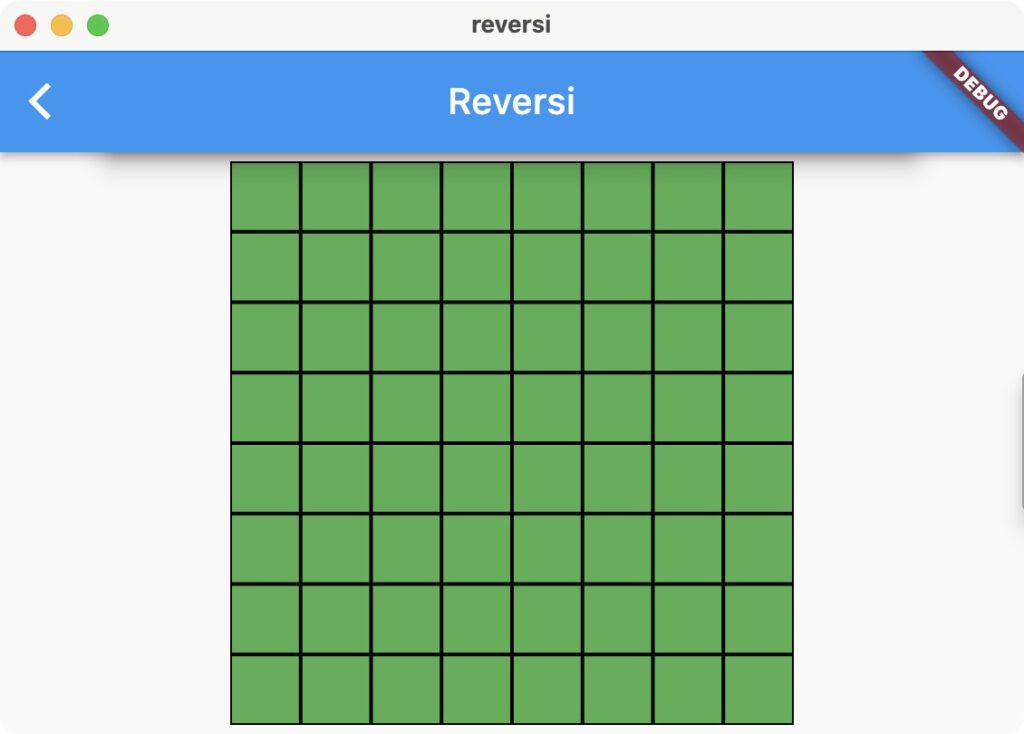
8行×8列分の領域を作って、中を緑で塗りつぶしています。
class _GameWidgetState extends State<GameWidget> {
...
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: const Text('Reversi'),
),
body: Center(
child: _buildBoard(context),
),
);
}
/// 盤面を表示する
Widget _buildBoard(BuildContext context) {
final double boardSize = _getBoardSize(context);
int rows = _gameLogic.boardRows;
int columns = _gameLogic.boardColumns;
return Container(
margin: const EdgeInsets.all(5.0),
color: Colors.black,
width: boardSize,
height: boardSize,
child: Column(children: <Widget>[
for (int row = 0; row < rows; row++) ... {
Expanded(
child: Row(
children: <Widget> [
for (int column = 0; column < columns; column++) ... {
Expanded(
child: Container(
margin: const EdgeInsets.all(1.0),
color:Colors.green,
),
)
}
]
)
)
}
])
);
}
}石の表示
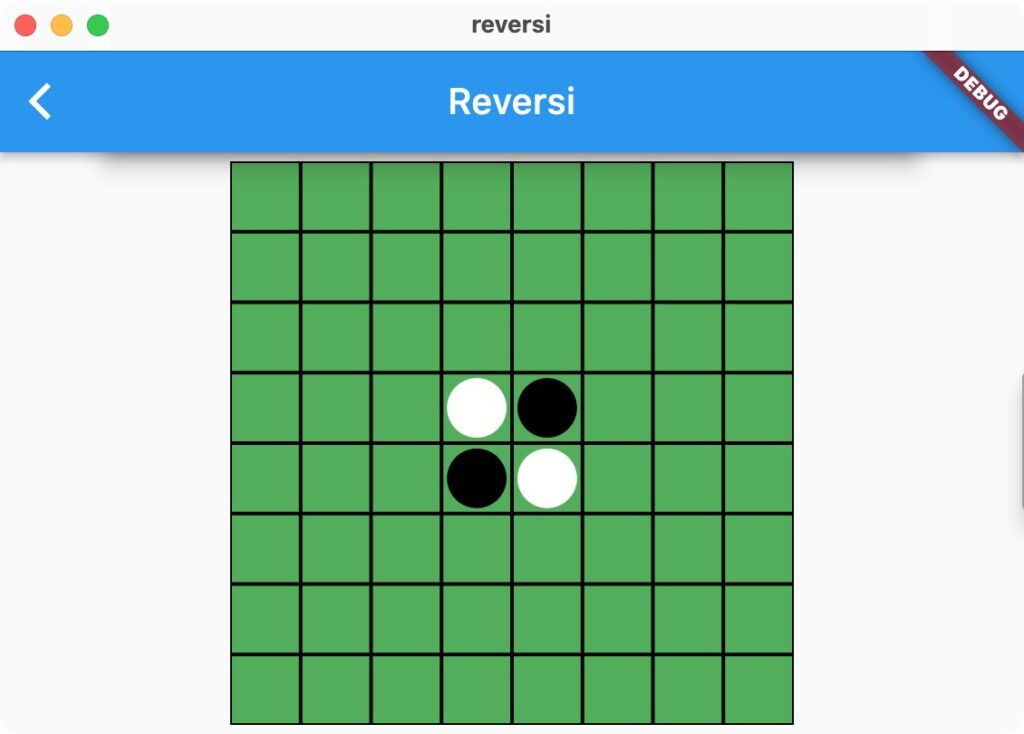
丸い石を表示したいのですが、四角を表示するBoxDecorationを利用します。borderRadiusに角丸の半径を設定することで、丸くできます。
Widget _buildStone(BuildContext context, int row, int column) {
final double boardSize = _getBoardSize(context);
final double squareSize = boardSize / _gameLogic.boardRows;
final Stone stone = _gameLogic.getStone(row, column);
if (stone == Stone.blank) {
return Container();
}
else {
return Container (
margin: const EdgeInsets.all(2.0),
decoration: BoxDecoration(
borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(squareSize/2),
color: stone == Stone.black ? Colors.black : Colors.white,
),
);
}
}
盤面に石を表示させます。
Widget _buildBoard(BuildContext context) {
final double boardSize = _getBoardSize(context);
int rows = _gameLogic.boardRows;
int columns = _gameLogic.boardColumns;
return Container(
margin: const EdgeInsets.all(5.0),
color: Colors.black,
width: boardSize,
height: boardSize,
child: Column(children: <Widget>[
for (int row = 0; row < rows; row++) ... {
Expanded(
child: Row(
children: <Widget> [
for (int column = 0; column < columns; column++) ... {
Expanded(
child: Container(
margin: const EdgeInsets.all(1.0),
color:Colors.green,
child: _buildStone(context, row, column),
),
)
}
]
)
)
}
])
);
}石をおくボタンの表示
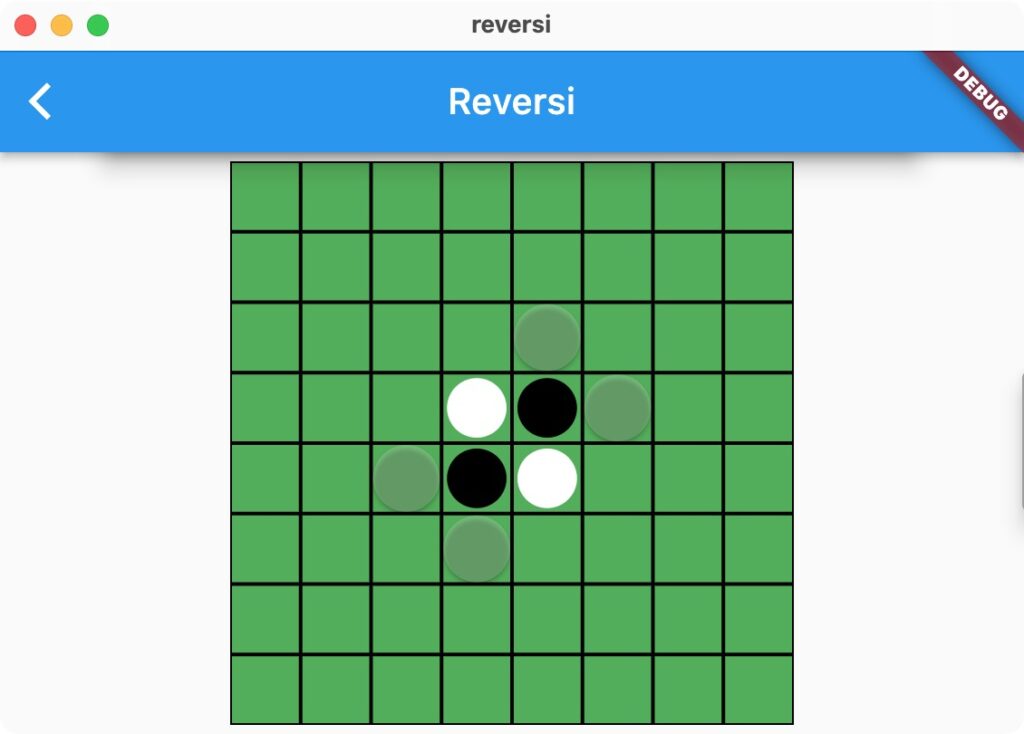
Stone.blackHintかStone.whiteHintのときにボタンを表示します。あまり主張したくないので、.withOpacity(0.2)で半透明にしています。
onPressedでボタンが押されたときのコールバックを呼び出します。説明は次項で行います。
Widget _buildStone(BuildContext context, int row, int column) {
final double boardSize = _getBoardSize(context);
final double squareSize = boardSize / _gameLogic.boardRows;
final Stone stone = _gameLogic.getStone(row, column);
if (stone == Stone.blank) {
return Container();
}
else if (stone == Stone.blackHint || stone == Stone.whiteHint) {
final Color stoneColor = stone == Stone.blackHint ? Colors.black : Colors.white;
return SizedBox(
width: squareSize,
height: squareSize,
child: ElevatedButton (
style: ElevatedButton.styleFrom(shape: const CircleBorder(), backgroundColor: stoneColor.withOpacity(0.2)),
child: const Text(''),
onPressed: () { _putStone(row, column); },
),
);
}
else {
return Container (
margin: const EdgeInsets.all(2.0),
decoration: BoxDecoration(
borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(squareSize/2),
color: stone == Stone.black ? Colors.black : Colors.white,
),
);
}
}ボタンが押されたら石を置いて、挟んだ石を裏返す
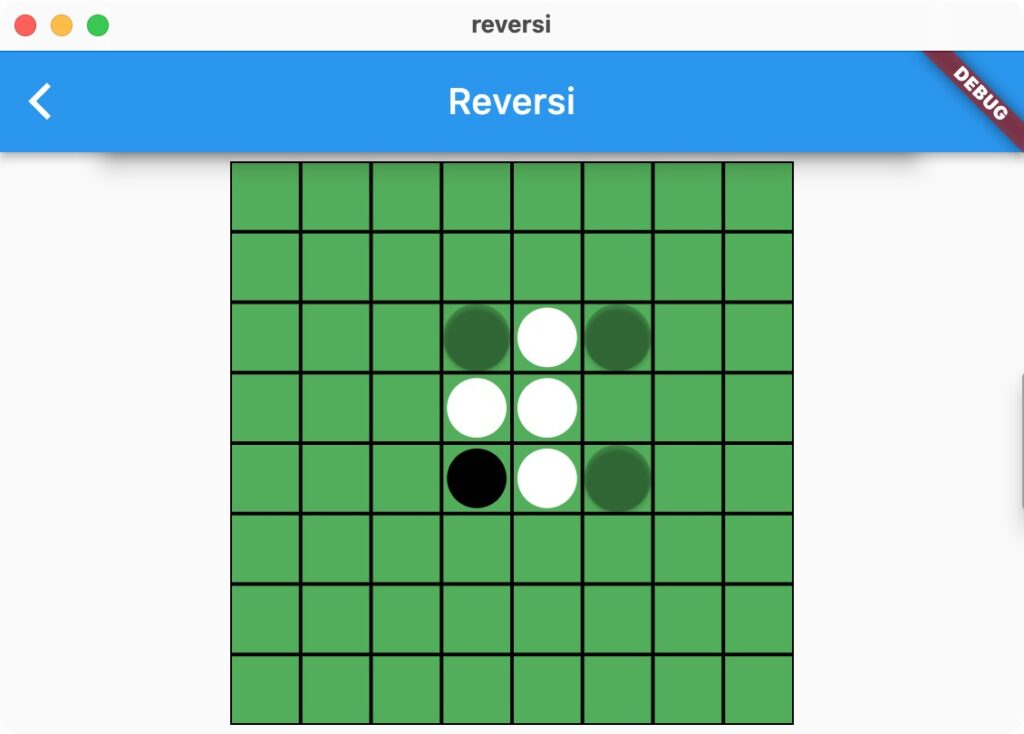
ボタンが押されたら、挟んだ石を裏返します。setState()は表示を更新する関数です。GameLogicの盤面の状態を変更するので、それに合わせて画面を再描画します。
void _putStone(int row, int column){
List<Position> reversePositions = _gameLogic.getReversePositions(row, column, _gameLogic.turn);
if (reversePositions.isNotEmpty) {
setState(() {
// ヒントをクリア
_gameLogic.clearHint();
// 石を置く
_gameLogic.putStone(row, column, _gameLogic.turn);
// はさんだ石を裏返す
for (Position position in reversePositions) {
_gameLogic.reverseStone(position.row, position.column);
}
// 次のターンへ
_gameLogic.changeTurn();
// ヒントを表示する
_gameLogic.hint();
});
}
}FlipCardで石を裏返すアニメーションをつける
パッと表示が変わると味気ないので、石を裏返すアニメーションをつけます。ちょうど良いflip_cardパッケージがありましたので、それを使用します。あるものは使って楽をするのがプログラマーのサガです。
flip_cardを使えるようにpubspec.yamlにパッケージを追加します。pubspec.yamlを開いてflip_card: ^0.7.0を追加するだけです。これで準備完了です。
dependencies:
flutter:
sdk: flutter
flip_card: ^0.7.0カードを裏返すためのコントローラーを初期化します。ちょっと勿体無いですけど、8×8マス分のコントローラーを作成しています。
class _GameWidgetState extends State<GameWidget> with TickerProviderStateMixin {
...
late List<List<FlipCardController>> _stoneFlipControllers;
@override
initState() {
...
// 石を裏返すためのコントローラーを生成
_stoneFlipControllers = List.generate(
_gameLogic.boardRows,
(int index) => List.generate(
_gameLogic.boardColumns,
(int index) => FlipCardController()
)
);
..
}石の表示にFlipCardを使います。FlipCardは表面と裏面の表示物を設定します。
direction: FlipDirection.HORIZONTALは水平方向に裏返す設定です。垂直方向にも裏返すことができます。
controller: _stoneFlipControllers[row][column]でコントローラーを割り当てます。
speed: 200は裏返す時間(ミリ秒)です。
Widget _buildStone(BuildContext context, int row, int column) {
...
if (stone == Stone.blank) {
...
}
else if (stone == Stone.blackHint || stone == Stone.whiteHint) {
...
}
else {
return FlipCard(
direction: FlipDirection.HORIZONTAL,
controller: _stoneFlipControllers[row][column],
speed: 200,
flipOnTouch: false,
front: Container (
margin: const EdgeInsets.all(2.0),
decoration: BoxDecoration(
borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(squareSize/2),
color: stone == Stone.black ? Colors.black : Colors.white,
),
),
back: Container (
margin: const EdgeInsets.all(2.0),
decoration: BoxDecoration(
borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(squareSize/2),
color: stone == Stone.black ? Colors.white : Colors.black,
),
),
);
}
}_putStoneにアニメーションを追加します。アニメーションを時系列順に行っていくために、非同期処理に変更しました。
非同期処理の解説は別途記事を用意します。
Future<void> _putStone(int row, int column) async {
if (_animationPlaying) {
return;
}
List<Position> reversePositions = _gameLogic.getReversePositions(row, column, _gameLogic.turn);
if (reversePositions.isNotEmpty) {
_animationPlaying = true;
setState(() {
// ヒントをクリアする
_gameLogic.clearHint();
// 石をおく
_gameLogic.putStone(row, column, _gameLogic.turn);
});
// 200ミリ秒待機
await Future.delayed(const Duration(milliseconds: 200));
for (Position position in reversePositions) {
// 挟んだ石を裏返すアニメーションを開始する
_stoneFlipControllers[position.row][position.column].toggleCard();
// 250ミリ秒待機
await Future.delayed(const Duration(milliseconds: 250));
setState(() {
// 内部的に石を裏返す
_gameLogic.reverseStone(position.row, position.column);
// FlipCardの表と裏が逆になるので、アニメーションなしでカードを裏返しておく
_stoneFlipControllers[position.row][position.column].toggleCardWithoutAnimation();
});
}
// 200ミリ秒待機
await Future.delayed(const Duration(milliseconds: 200));
setState(() {
// 次のターンへ
_gameLogic.changeTurn();
// ヒントを表示する
_gameLogic.hint();
});
}
}現在のターンをカードで表示
ターン切り替え時に、次はどちらのターンなのかをカードで表示します。
カードをアニメーションさせるために、AnimationとAnimationControllerを初期化します。
class _GameWidgetState extends State<GameWidget> with TickerProviderStateMixin {
...
late Animation<double> _turnCardAnimation;
late AnimationController _turnCardAnimationController;
@override
initState() {
...
// ターンをあらわすカードのアニメーション
_turnCardAnimationController = AnimationController(
duration: const Duration(milliseconds: 1000),
vsync: this,
);
_turnCardAnimation = TweenSequence<double>([
// 左から中央にきて
TweenSequenceItem<double>(
tween: Tween(begin: 0.0, end: 0.5).chain(CurveTween(curve: Curves.ease)),
weight: 15,
),
// 一定時間停止して
TweenSequenceItem<double>(
tween: ConstantTween<double>(0.5),
weight: 70,
),
// 中央から右にはける
TweenSequenceItem<double>(
tween: Tween(begin: 0.5, end: 1.0).chain(CurveTween(curve: Curves.ease)),
weight: 15,
),
]).animate(_turnCardAnimationController)
..addListener(() {
setState(() {});
})
..addStatusListener((status) {
if (status == AnimationStatus.completed) {
// アニメーションが終わったら次の順番のヒントを表示する
_animationPlaying = false;
_gameLogic.hint();
}
});
...
// 最初のターンの通知
_animationPlaying = true;
Future.delayed(const Duration(seconds: 1), () {
_turnCardAnimationController.forward();
});
}
...
}カードを表示するWidgetを生成します。
Widget _buildTurnCard(BuildContext context) {
final double cardWidth = _getBoardSize(context) / 2;
final double cardHeight = cardWidth / 2;
final double fontSize = cardWidth / 8;
final Size screenSize = _getScreenSize(context);
final distance = screenSize.width + cardWidth ;
final double x = -cardWidth -5 + _turnCardAnimation.value * distance ;
final double y = screenSize.height / 2 - cardHeight / 2 - 5;
return Positioned(
left: x,
top: y,
child: Card(
color: Colors.grey,
elevation: 10,
shadowColor: Colors.black,
child: SizedBox(
width: cardWidth,
height: cardHeight,
child: Center(
child: Text(
'● の番です。',
style: TextStyle(
fontSize: fontSize,
color: _gameLogic.turn == Stone.black ? Colors.black : Colors.white,
)
)
),
)
)
);
}盤面の上に表示したいので、Stackを利用します。
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: const Text('Reversi'),
),
body: Stack(
children: <Widget>[
Center(
child: _buildBoard(context),
),
_buildTurnCard(context),
],
),
);
}石をおいたときに、ターン表示のアニメーションを行うようにします。
Future<void> _putStone(int row, int column) async {
...
setState(() {
if (_gameLogic.changeTurn()) {
// 次のターンのカードを表示
_turnCardAnimationController.reset();
_turnCardAnimationController.forward();
}
});
...
}ゲーム終了のカードを表示
こちらもターン表示と同様にカードで表示します。
カードをアニメーションさせるために、AnimationとAnimationControllerを初期化します。
class _GameWidgetState extends State<GameWidget> with TickerProviderStateMixin {
...
late Animation<double> _finishCardAnimation;
late AnimationController _finishCardAnimationController;
@override
initState() {
...
// 終了アニメーション
_finishCardAnimationController = AnimationController(
duration: const Duration(milliseconds: 500),
vsync: this,
);
_finishCardAnimation = TweenSequence<double>([
TweenSequenceItem<double>(
tween: Tween(begin: 0.0, end: 0.5).chain(CurveTween(curve: Curves.easeIn)),
weight: 60,
),
TweenSequenceItem<double>(
tween: Tween(begin: 0.5, end: 0.4).chain(CurveTween(curve: Curves.easeOut)),
weight: 20,
),
TweenSequenceItem<double>(
tween: Tween(begin: 0.4, end: 0.5).chain(CurveTween(curve: Curves.easeIn)),
weight: 20,
),
]).animate(_finishCardAnimationController)
..addListener(() {
setState(() {});
});
...
}
}カードを生成するWidgetを生成します。
Widget _buildFinishCard(BuildContext context) {
final Size screenSize = _getScreenSize(context);
final double cardWidth = screenSize.width * 0.8;
final double cardHeight = cardWidth * 0.5;
final double titleSize = cardWidth / 8;
final double fontSize = titleSize * 0.7;
final distance = screenSize.height + cardHeight;
final double x = (screenSize.width - cardWidth) / 2 - 5;
final double y = -cardHeight -5 + distance * _finishCardAnimation.value;
int numberOfWhite = _gameLogic.numberOfStone(Stone.white);
int numberOfBlack = _gameLogic.numberOfStone(Stone.black);
String result = numberOfWhite != numberOfBlack ? '● のかち' : 'ひきわけ';
Color resultColor = numberOfWhite > numberOfBlack ? Colors.white : Colors.black;
return Positioned(
left: x,
top: y,
child: Card(
color: Colors.grey.withOpacity(0.8),
elevation: 10,
shadowColor: Colors.black,
child: SizedBox(
width: cardWidth,
height: cardHeight,
child: Column(
children: <Widget> [
Text(
result,
style: TextStyle(
fontSize: titleSize,
color: resultColor,
),
),
Text(
'●:$numberOfWhite',
style: TextStyle(
fontSize: fontSize,
color: Colors.white,
),
),
Text(
'●:$numberOfBlack',
style: TextStyle(
fontSize: fontSize,
color: Colors.black,
),
),
],
),
)
)
);
}盤面の上に表示したいので、Stackを利用します。
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: const Text('Reversi'),
),
body: Stack(
children: <Widget>[
Center(
child: _buildBoard(context),
),
_buildTurnCard(context),
_buildFinishCard(context),
],
),
);
}ゲーム終了時にカードを表示します。
Future<void> _putStone(int row, int column) async {
...
setState(() {
if (_gameLogic.changeTurn()) {
// 次のターンのカードを表示
_turnCardAnimationController.reset();
_turnCardAnimationController.forward();
} else {
// ゲームオーバー
_finishCardAnimationController.forward();
}
});
...
}どちらかが勝ったら紙吹雪をちらす
カードの表示だけだと味気ないので、どちらかが勝ったときに紙吹雪をちらします。ちょうど良いconfettiパッケージがありましたので、それを使用します。
confettiを使えるようにpubspec.yamlにパッケージを追加します。pubspec.yamlを開いてconfetti: ^0.6.0-nullsafetysを追加するだけです。これで準備完了です。
dependencies:
flutter:
sdk: flutter
flip_card: ^0.7.0
confetti: ^0.6.0-nullsafetys紙吹雪のコントローラーを初期化します。
class _GameWidgetState extends State<GameWidget> with TickerProviderStateMixin {
...
late ConfettiController _confettiController;
@override
initState() {
...
// 紙吹雪のコントローラーの初期化
_confettiController = ConfettiController(
duration: const Duration(milliseconds: 500),
);
...
}
...
}紙吹雪のWidgetを生成します。
Widget _buildConfetti(BuildContext context) {
final double boardSize = _getBoardSize(context);
final double minSize = boardSize * 0.02;
final double maxSize = minSize * 2;
final Size screenSize = _getScreenSize(context);
return Positioned(
left: screenSize.width / 2,
top: -maxSize,
child: ConfettiWidget(
confettiController:_confettiController,
blastDirectionality: BlastDirectionality.directional,
blastDirection: -pi / 2,
emissionFrequency: 0.5,
numberOfParticles: 5,
shouldLoop: true,
maxBlastForce: 4,
minBlastForce: 2,
displayTarget: false,
minimumSize: Size(minSize, minSize),
maximumSize: Size(maxSize, maxSize),
gravity: 0.0981,
particleDrag: 0.001,
),
);
}ゲーム終了時に紙吹雪をちらします。
Future<void> _putStone(int row, int column) async {
...
setState(() {
if (_gameLogic.changeTurn()) {
// 次のターンのカードを表示
_turnCardAnimationController.reset();
_turnCardAnimationController.forward();
} else {
// ゲームオーバー
_finishCardAnimationController.forward();
if (_gameLogic.numberOfStone(Stone.white) != _gameLogic.numberOfStone(Stone.black)) {
_confettiController.play();
}
}
});
...
}まとめ
長い記事でしたが、最後まで読んでくれてありがとうございます。
プログラムを学ぶ際には、基礎学習の時間を短めにして、とりあえず何かを作ってみるのがおすすめです。必要に迫られたタイミングで部分的に学んでいくことで、学習効率が劇的によくなります。
ぜひあなたも何か作ってみてください。

コメント